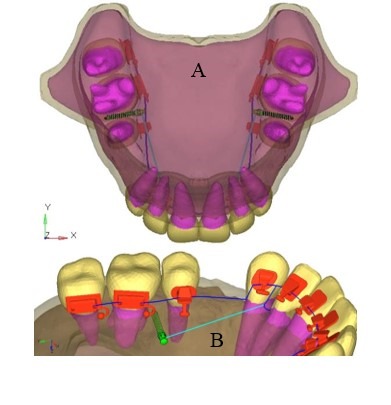
Background. This research aimed to judge and analyze the distribution of stresses on the palatal micro-implants and the cortical bone at the micro-implant web site with optimum orthodontic retraction drive in lingual orthodontics.
Methods. ANSYS 12.1 software program was used to assemble the finite ingredient mannequin of the maxillary bone, enamel and the periodontal ligament together with the lingual bracket set-up with wire and the micro-implant. Six- and 8-mm micro-implants have been constructed.
The last mannequin consisted of 99190 nodes and 324364 parts. A 200-gram of retraction drive was utilized from the micro-implant to the anterior retraction hook. The micro-implant was embedded between the second premolar and the first molar. Hyper-view software program was used to get the outcomes in X-Y-Z dimensions.
Results. The most von Mises stresses detected have been 52.543 MPa for 6-mm micro-implant and 54.489 MPa for 8-mm micro-implant. Maximum stress was at the neck of the micro-implant. The 8-mm implant mannequin confirmed 6×10-3 mm of lingual displacement.
The least displacement of 1×10-3 mm was observed for each the implant fashions in the apico-occlusal course. The most von Mises stresses in the cortical bone at the micro-implant web site was 18.875 MPa for 6-mm micro-implant and 21.551 MPa for 8-mm micro-implant.
Conclusion. Six-mm micro-implant might be the selection for the implant-supported lingual orthodontic retraction because it produced minimal stresses on the cortical bone, and the preliminary stress displacements produced on the micro-implant have been additionally minimal.

Research priorities for the administration of damaged bones of the higher limb in individuals over 50: a UK precedence setting partnership with the James Lind Alliance.
To decide analysis priorities for the administration of damaged bones of the higher limb in individuals over 50, which signify the shared priorities of sufferers, their households, carers and healthcare professionals.A nationwide (UK) analysis precedence setting partnership.People aged 50 and over who’ve skilled a fracture of the higher limb, carers concerned in their care, household and mates of sufferers, healthcare professionals concerned in the remedy of these sufferers.
Using a multiphase methodology in partnership with the James Lind Alliance over 15 months (September 2017 to December 2018), a nationwide scoping survey requested respondents to submit their analysis uncertainties. These have been amalgamated right into a smaller quantity of analysis questions.
The current proof was searched to make sure that the questions had not already been answered. A second nationwide survey requested respondents to prioritise the analysis questions.
A last shortlist of 25 questions was taken to a multi-stakeholder workshop the place a consensus was reached on the prime 10 priorities.There have been 1898 unique uncertainties submitted by 328 respondents to the first survey. These unique uncertainties have been refined into 51 analysis questions of which 50 have been judged to be true uncertainties following a evaluation of the analysis proof. There have been 209 respondents to the second (interim prioritisation) survey.
The prime 10 priorities embody a broad vary of uncertainties in administration and rehabilitation of higher limb fractures.The prime 10 UK analysis priorities spotlight uncertainties in how we assess outcomes, present data, obtain ache management, rationalise surgical intervention, optimise rehabilitation and present psychological help. The breadth of these analysis areas highlights the worth of this system.
This work ought to assist to steer analysis in this space for the subsequent 5-10 years and the problem for researchers now could be to refine and ship solutions to those analysis priorities.
