To consider the diagnostic accuracy of the Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT) in the research of the bone marrow edema.
The MRI pictures of 100 sufferers with episodes of articular and or bone pains with or with out traumatic lesion have been prospectively evaluated throughout a interval between March 2018 and February 2019. In the presence of bone marrow edema, a DECT was carried out.
The measurement of the density of the bone marrow edema in the DECT was in contrast with wholesome bone in the similar affected person by two operators.
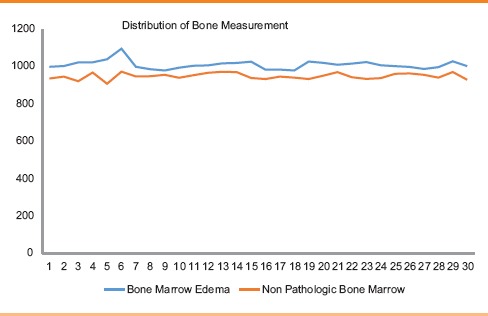
ResultThe DECT and MRI pictures of 15 sufferers with bone marrow edema have been in contrast. The imply of pathologic bone marrow edema was 1008.20 (Standard Deviation (SD) 23.00), for wholesome bone marrow 947.53 (SD 16.42), and t = 11.75, with a statistical significance P < 0.05 (Statistical significance 95%).
The settlement between the measurements of the two radiologists has a statistical significance (P < 0.05).The DECT presents a superb diagnostic accuracy to detect the bone marrow edema, akin to MRI. The utility of these latest prospects is most the place entry to MRI continues to be very tough.

Usefulness of Mesenchymal Cell Lines for Bone and Cartilage Regeneration Research.
The unavailability of enough numbers of human major cells is a serious roadblock for in vitro restore of bone and/or cartilage, and for performing illness modelling experiments. Immortalized mesenchymal stromal cells (iMSCs) could also be employed as a research device for avoiding these issues.
The objective of this evaluate was to revise the accessible literature on the traits of the iMSC traces, paying particular consideration to the upkeep of the phenotype of the major cells from which they have been derived, and whether or not they’re successfully helpful for in vitro illness modeling and cell remedy functions.
This evaluate was carried out by looking on Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed databases from 1 January 2015 to 30 September 2019.
The key phrases used have been ALL = (mesenchymal AND (“cell line” OR immortal*) AND (cartilage OR chondrogenesis OR bone OR osteogenesis) AND human). Only authentic research research during which a human iMSC line was employed for osteogenesis or chondrogenesis experiments have been included.
After describing the success of the immortalization protocol, we targeted on the iMSCs upkeep of the parental phenotype and multipotency. According to the literature revised, evidently the upkeep of these traits will not be assured by immortalization, and that cautious choice and validation of clones with explicit traits is important for taking benefit of the full potential of iMSC to be employed in bone and cartilage-related research.
